It started in the dead of winter. My mom could not find that heavy jacket she had packed away last year. We turned the house upside down, but it was nowhere to be found.
I realized I had the same problem. I’m constantly looking for that specific square piece of wood, a box of 2.5-inch galvanized screws, or where I left my IRFZ44N MOSFET transistors for a circuit I was building.
That frustration sparked “Where is my Thing?” — a Spatial Memory Agent designed to act as an external hippocampus for your physical possessions.
Try it live at things.utkarshjoshi.com.
🏗️ Architecture Overview
The system follows a modern client-server architecture optimized for real-time voice interaction.
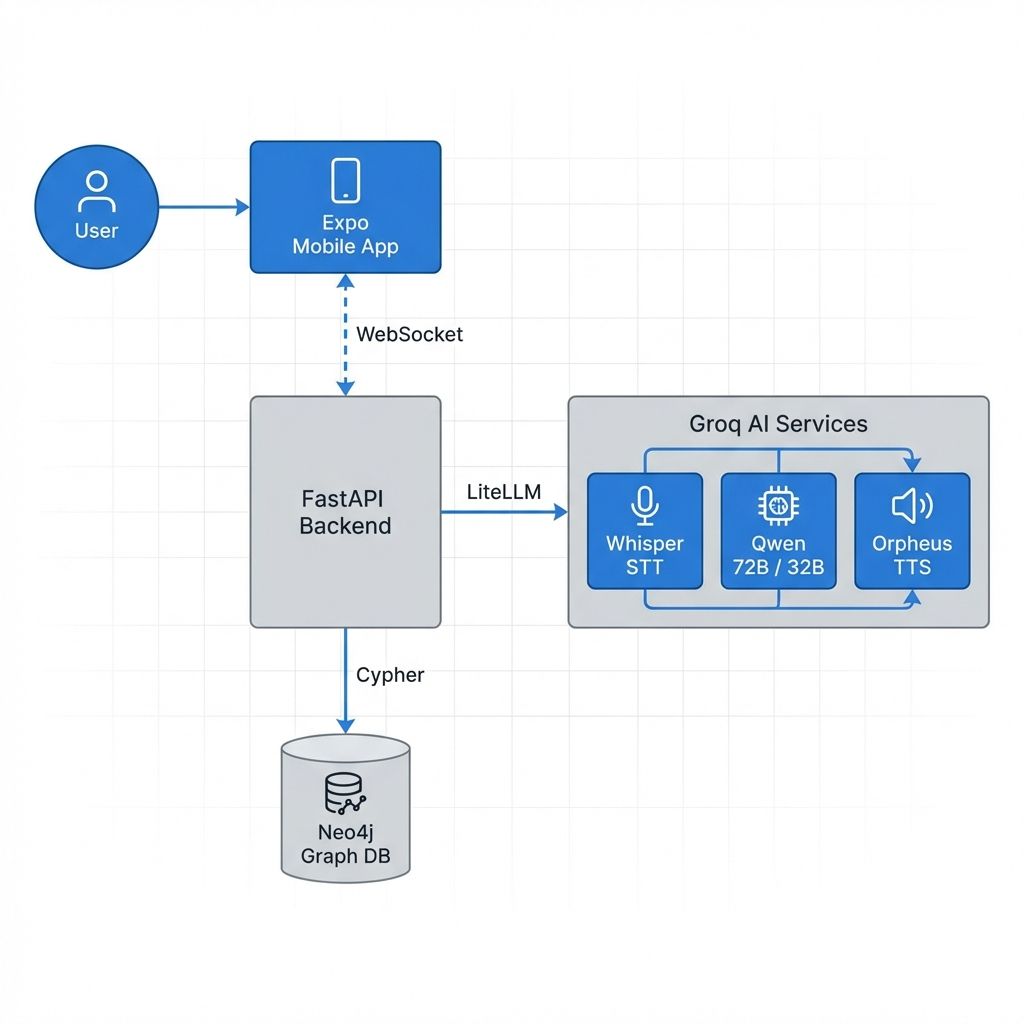
🎙️ Voice & Agent Implementation
The core of the experience is the Voice Agent, implemented using Google ADK (Agent Development Kit) and Groq.
Technical Pipeline:
- Audio Capture:
useVoiceAgent.tscaptures audio from the microphone using expo-av. - WebSocket Streaming: Audio chunks are sent as Base64-encoded PCM/WebM to the backend over a persistent WebSocket connection.
- Speech-to-Text: The backend (
voice.py) uses Groq’s Whisper model for low-latency transcription. - Agent Reasoning: The transcribed text is processed by a Spatial Memory Agent built on Google ADK.
- Spatial Tools: The agent uses natural language to trigger specialized tools:
remember_thing: Updates the Neo4j graph with new item locations.find_thing: Queries Neo4j using fuzzy search across names, descriptions, and tags.move_thing: Updates relationship edges in the graph.list_contents: Traverses the graph to find all items in a specific location path.
- Text-to-Speech: The agent’s response is converted to audio using Orpheus TTS (via Groq).
- Playback: The frontend receives the audio and plays it back with a 1.25x speed multiplier to ensure a snappy, conversational feel.
🎨 Frontend (Expo Web)
The frontend is a premium Expo (React Native) application, currently optimized for Web deployment.
Key Features:
- Visual Orb: A state-aware
VoiceOrbthat reflects the agent’s state (listening, thinking, speaking). It features multiple styles including a premium Liquid Blob (“AIOrb”). - Knowledge Graph: A fully interactive SVG-based graph visualizing spatial relationships. It uses a custom Force-Directed Layout simulation for node positioning.
- Aesthetics: Glassmorphism, modern typography (Inter), and custom color palettes defined in
theme.ts. - Authentication: Integrated with Clerk for secure user sessions and JWT-based WebSocket authentication.
⚙️ Backend & Infrastructure
Technical Stack:
- FastAPI: High-performance Python framework for API and WebSockets.
- Neo4j: Graph database used as the “Long Term Memory” for spatial data, mapping items to rooms, containers, and zones.
- Docker: Containerized deployment for both API and Neo4j.
- Nginx: Reverse proxy with SSL handling via Certbot.
Socket Protocol: A custom JSON-over-WebSocket protocol:
type: audio: Binary audio data.type: transcript: Real-time text feedback for both user and assistant.type: tool_call: Notifies the UI when the agent is performing a specific action (e.g., “Reflecting on memory”).type: interrupt: Allows the system to immediately halt AI speech when the user speaks.
🧠 Spatial Memory Logic
The project implements a “Spatial Hierarchy” in Neo4j:
- Nodes: Thing (Item), Place (Room/Container/Shelf).
- Edges:
LOCATED_IN,ASSOCIATED_WITH,CONTAINS.
The agent understands paths like Kitchen > Drawer > Left Corner. When searching, it can find items based on partial matches and return the full path to the user.
Gallery

